Type 2 Diabetes
Diagnosis & Management
Diagnostic Criteria(i)
| Fasting plasma glucose mmol/L (mg/dL)(ii) |
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) 2 hours value mmol/L (mg/dL)(iii) |
HbA1c(iv) (mmol/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | ≥ 7.0 (126) OR | ≥ 11.1 (200) OR | ≥ 6.5 % (≥ 48) |
| Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) | < 7.0 (126) AND | 7.8 – 11.0 (140-199) | Prediabetes 5.7-6.4 % (39-47) |
| Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) | 5.7-6.9 AND (100-125) | < 7.8 (140) |
- As defined by WHO
- An abnormal finding should be repeated before confirming the diagnosis
- Recommended in persons with HIV with fasting blood glucose of 5.7 - 6.9 mmol/L (100-125 mg/dL) as it may identify persons with overt diabetes
- Do not use HbA1c in presence of haemoglobinopathies, increased erythrocyte turnover and severe liver or kidney dysfunction. Falsely high values are measured under supplementation with iron, vitamin C and E as well as older age (age > 70: HbA1c + 0.4%). HbA1c values in treated persons with HIV, particularly when on ABC, tend to underestimate type 2 diabetes. Both IGT and IFG increase CVD morbidity and mortality and increase the risk of developing diabetes by 4-6-fold. These persons should be targeted for lifestyle intervention, and their CVD risk factors must be evaluated and treated
Management
Use of Glucose-Lowering Medications in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes(i)
- These recommendations are derived from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) consensus report. Check national guidelines, where available
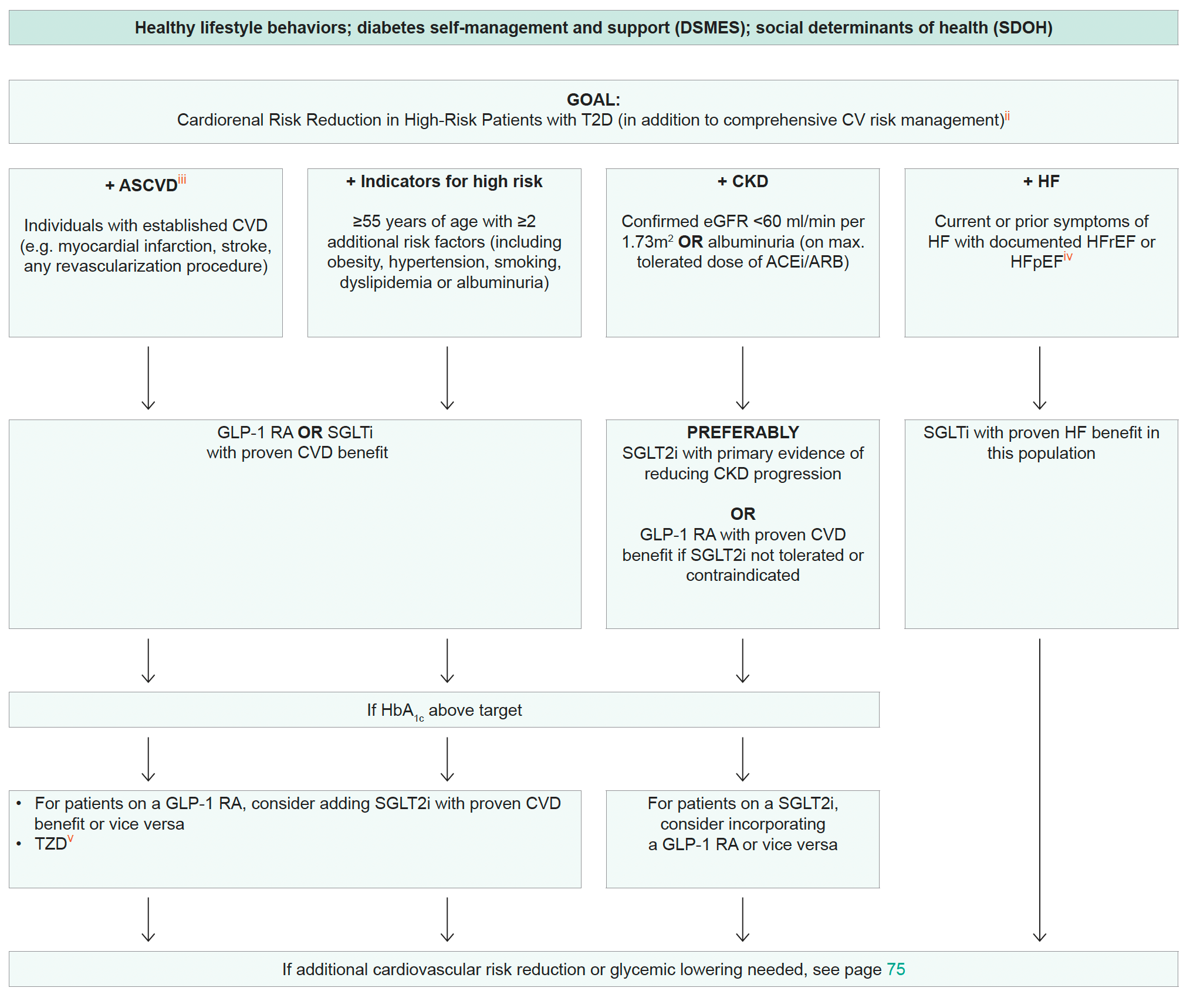
- In people with HF, CKD, established CVD or multiple risk factors for CVD, the decision to use GLP-1 RA or SGLT2i with proven benefit should be independent of the background use of metformin. The benefits of GLP-1 RA and SGLT2i for cardiovascular and renal outcomes have been found to be independent of metformin use, and thus these agents should be considered in people with established or high risk of CVD, HF, or CKD, independent of metformin use
- Defined differently across trials but all included individuals with established CVD. Variably included: conditions such as transient ischemic attack, unstable angina, amputation, symptomatic or asymptomatic coronary artery disease
- HFrEF, Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction; HFpEF, Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction
- Low-dose TZD may be better tolerated with similar efficacy
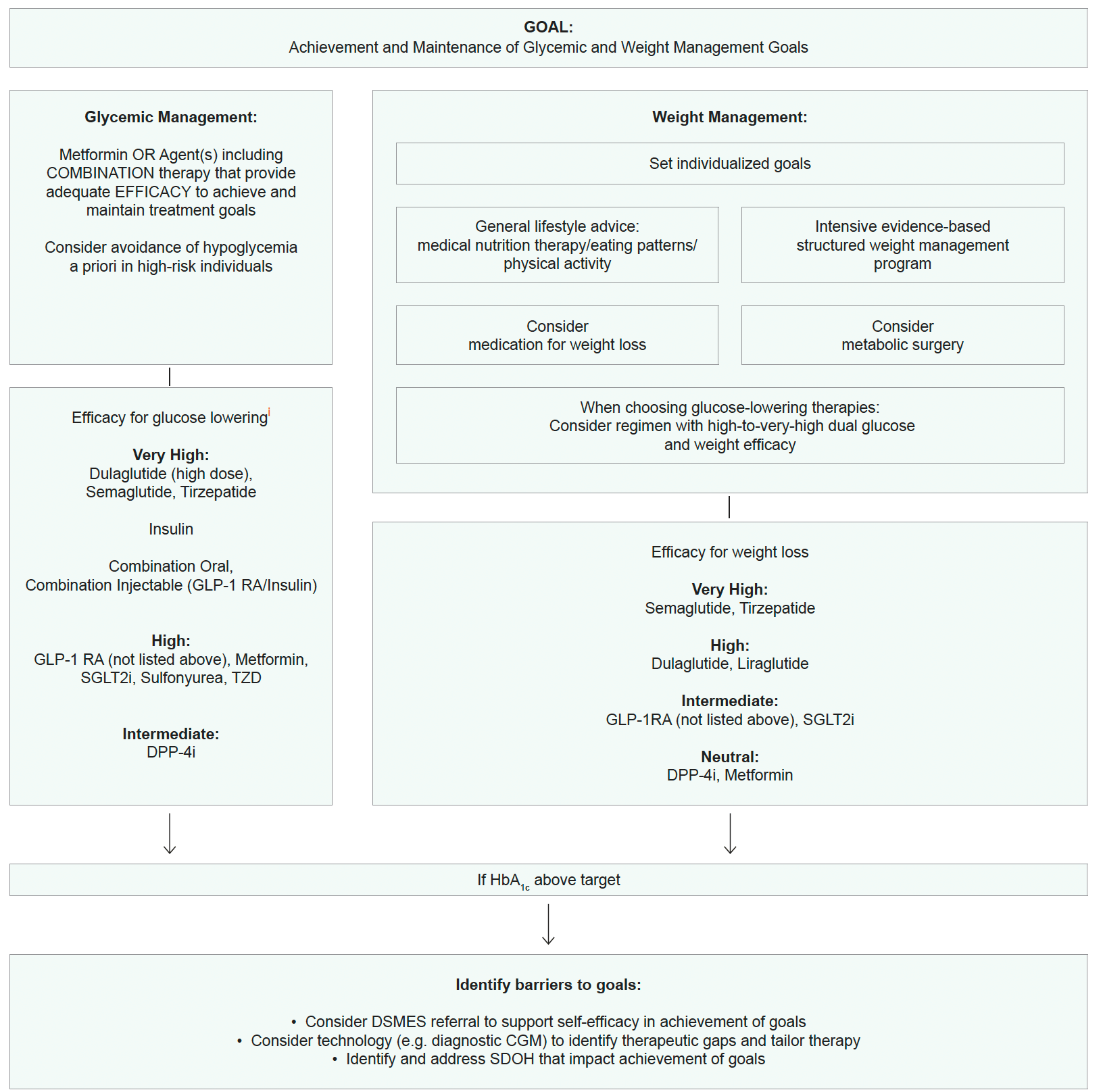
- In general, higher efficacy approaches have greater likelihood of achieving glycemic goals. Drugs listed may not be available in some countries. Consider referring to diabetologist or endocrinologist