Anti-infective Drugs for OIs and STIs and ARVs
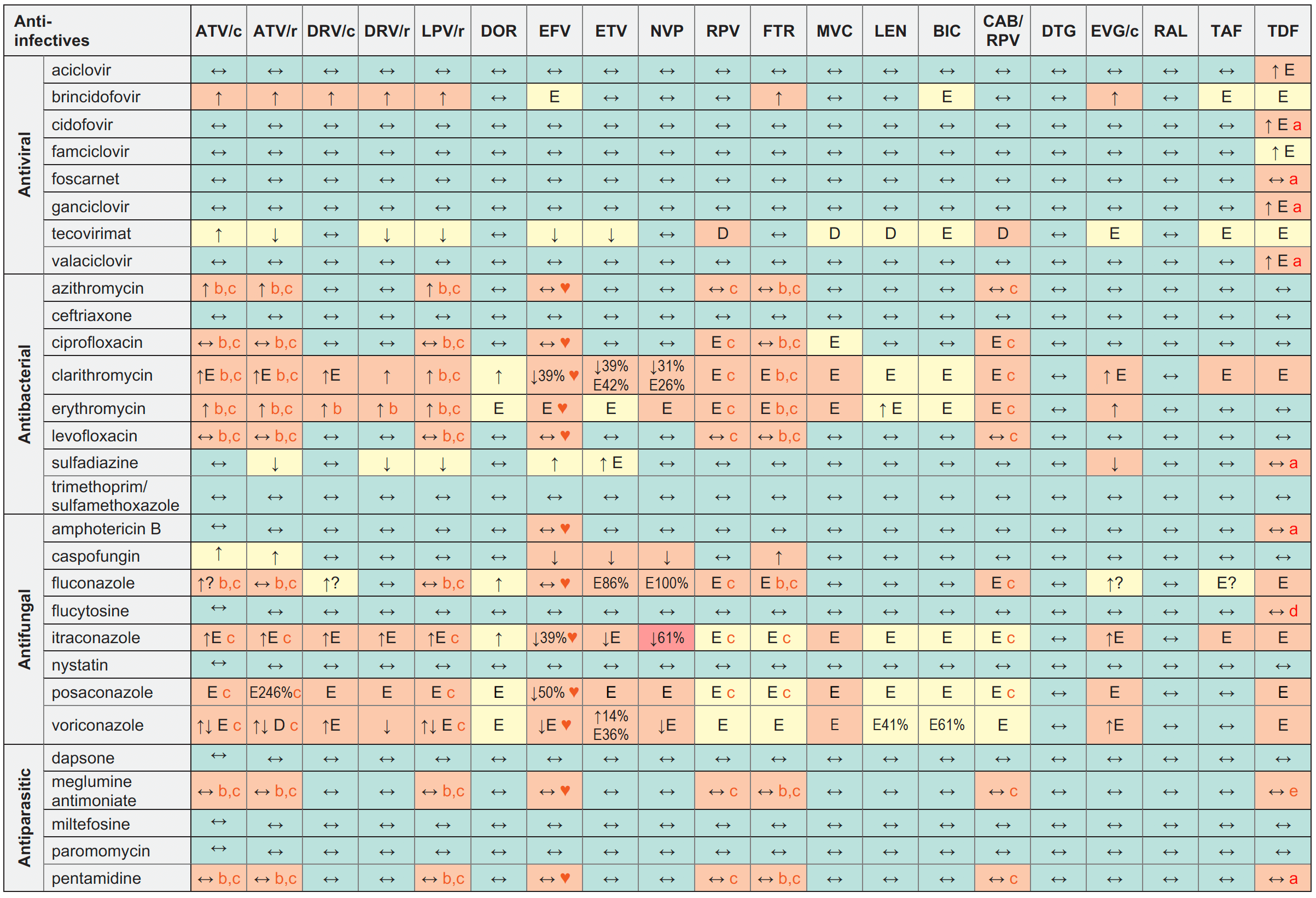
Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the anti-infective
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the anti-infective
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
Antibacterial
- Refer to the Anti-tuberculosis table for interactions with amikacin, moxifloxacin and rifabutin ;
- Refer to the Anti-malarial table for interactions with clindamycin and doxycycline.
Antiparasitic
Refer to the Anti-malarial table for interactions with atovaquone, primaquine and pyrimethamine.
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
FTC:
- Potential additive renal toxicity with sulfadiazine and flucytosine;
- Potential increased FTC exposure with trimethoprim, but no dose adjustment required in patients with
normal renal function;
- Potential additive renal toxicity with sulfadiazine and flucytosine;
- Increased 3TC exposure (43%) with trimethoprim, but no dose adjustment required in patients with normal renal function. Some trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole liquid preparations may contain sorbitol which decreases the bioavailability of lamivudine solutions
ZDV:
- Potential risk of additive haematoxicity with brincidofovir and flucytosine;
- Increased ZDV exposure (20%) with ganciclovir;
- Decreased ZDV exposure (12%) with clarithromycin;
- Potential increased risk of ZDV adverse reactions with trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, amphotericin B and flucytosine;
- Increased ZDV exposure (74%) with fluconazole. Routine ZDV dose modification not required, but monitor for potential ZDV toxicity;
- No PK interaction observed with dapsone but potential increased risk of ZDV adverse reactions;
- Potential increased risk of ZDV adverse reactions with pentamidine (but not with aerosolised pentamidine at doses used in prophylaxis)
Comments
- TDF should be avoided with concurrent or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent. If co-administration is unavoidable, monitor renal function closely.
- ECG monitoring is recommended.
- Caution as both drugs can induce QT interval prolongation.
- Co-administration could potentially increase haematological toxicity. Monitor haematological parameters and consider dose reduction if required.
- Renal impairment and sometimes fatal renal failure have been described with meglumine antimoniate treatment. Close monitoring of renal function is warranted.
♥ EFV prolonged the QT interval above the regulatory threshold of concern in homozygous carriers of the CYP2B6*6/*6 allele (516T variant). Coadministration with a drug with a known risk of TdP is contraindicated in the EFV European label.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
