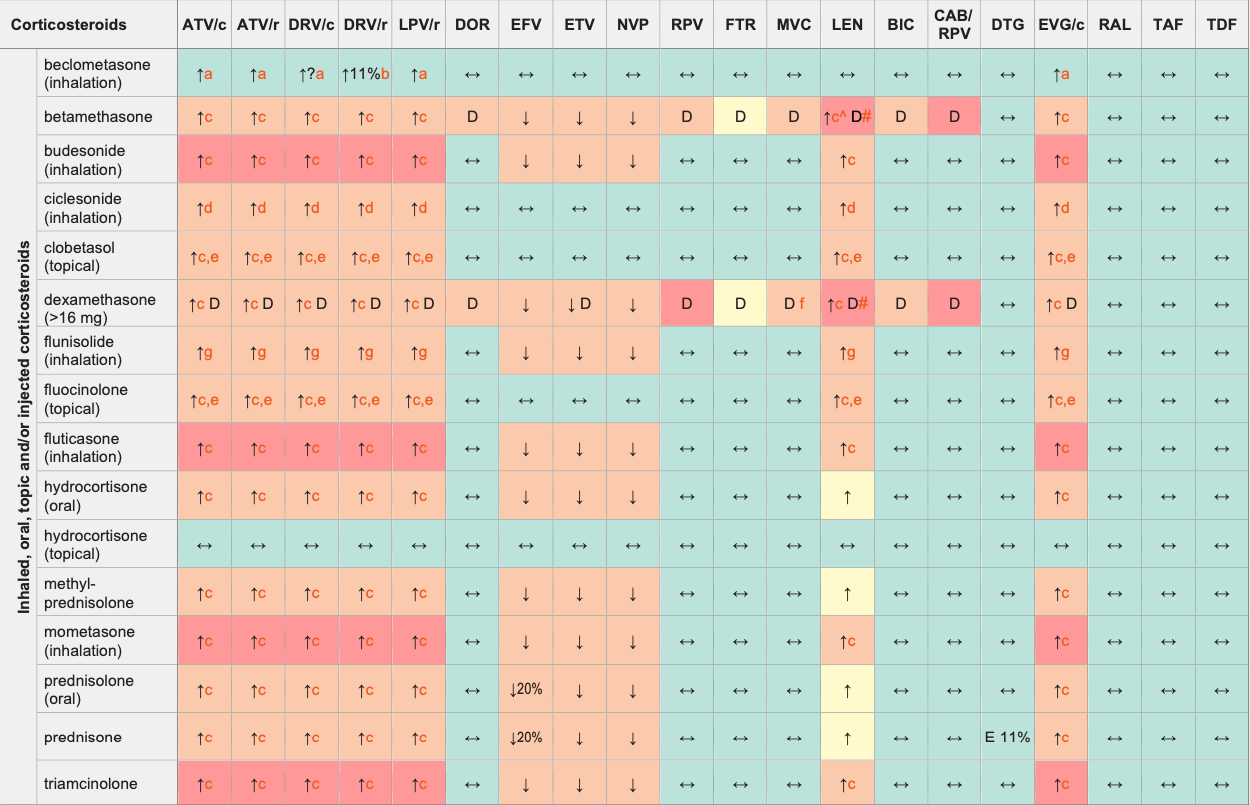
Corticosteroids & ARVs
Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the corticosteroid
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the corticosteroid
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV:
no clinically relevant interactions expected
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- Co-administration of RTV (100 mg bid) increased the concentrations of the active metabolite (beclometasone-17-monopropionate) but no significant effect on adrenal function was seen. Caution is still warranted, use the lowest possible corticosteroid dose and monitor for corticosteroid side effects.
- DRV/r decreased the exposure of active metabolite (beclometasone-17- monopropionate), no significant effect on adrenal function was seen.
- Risk of having elevated corticosteroid levels, Cushing's syndrome and adrenal suppression. This risk is present for oral and injected corticosteroid but also for topical, inhaled or eye drops administration.
- No dose adjustment required but monitor closely, especially for signs of Cushing's syndrome when using a high dose or prolonged administration.
- The extent of percutaneous absorption is determined by many factors such as degree of inflammation and alteration of the skin, duration, frequency and surface of application, use of occlusive dressings.
- Consider using MVC a dose of 600 mg bid with dexamethasone in the absence of a PI or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, particularly if dexamethasone is used at a high dose and in case of long-term treatment. Consider decreasing MVC to 150 mg bid with dexamethasone in presence of a protease inhibitor or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- Use the lowest possible flunisolide dose with monitoring for corticosteroid side effects.
^ LEN causes moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and, when discontinued, remains in the circulation for prolonged periods. Residual concentrations of LEN may affect the exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates and/or narrow therapeutic index drugs that are initiated within 9 months after the last subcutaneous dose of LEN.
# At least a 2-week (moderate inducers) or 4-week (strong inducers) cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of LEN due to the persisting inducing effect after discontinuation of an inducer.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
