Anticoagulants/Antiplatelet Agents & ARVs
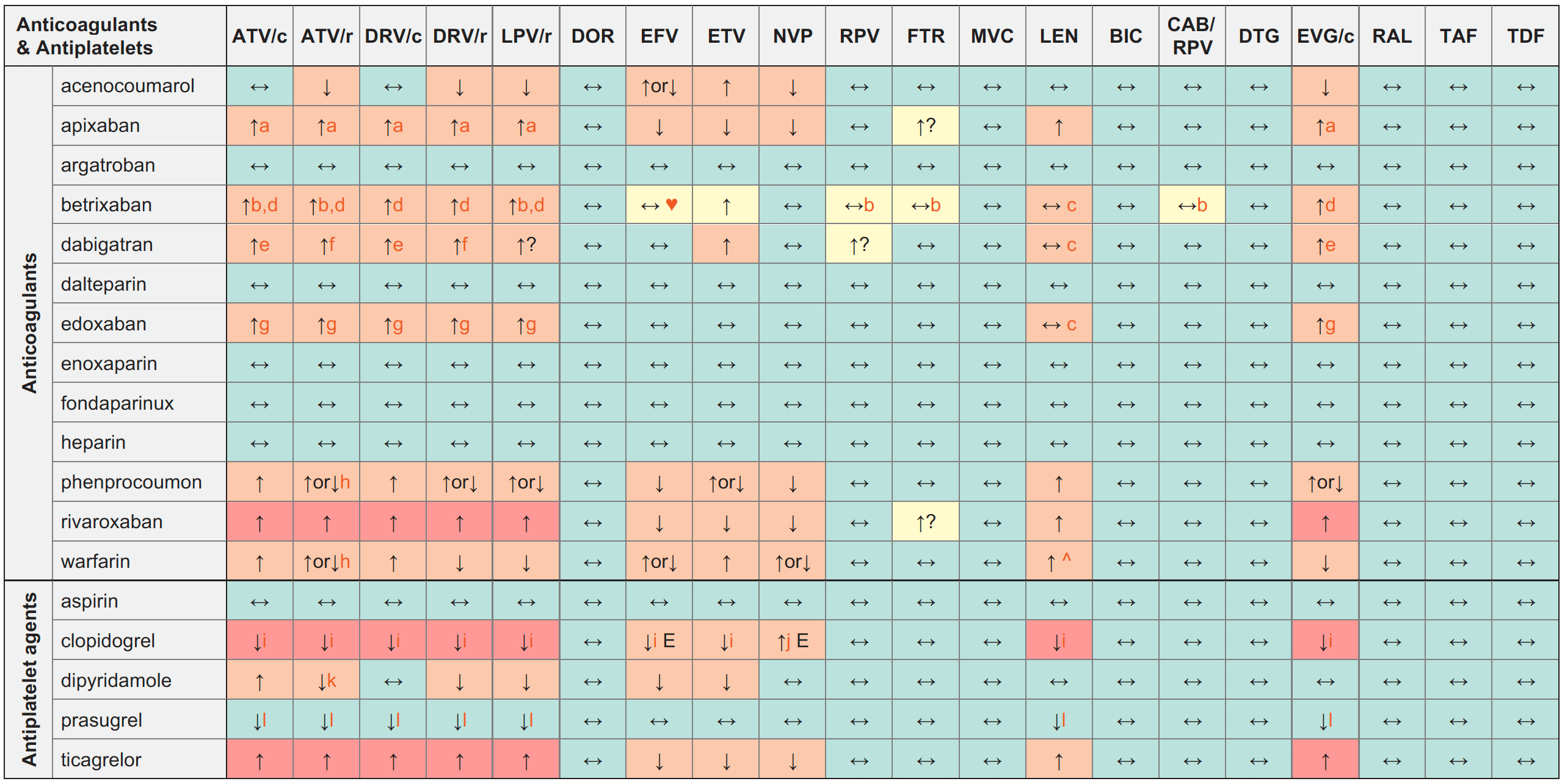
Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the anticoagulant/
antiplatelet agent
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the anticoagulant/
antiplatelet agent
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC:
May potentially reduce the pharmacodynamic effect of clopidogrel
FTC, 3TC, ZDV:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- US label suggests to use apixaban at a reduced dose (2.5 mg bid) if needed.
- Both drugs can potentially prolong the QT interval, ECG monitoring recommended.
- LEN is not considered to be a meaningful inhibitor of P-gp. No a priori dose adjustment of betrixaban, dabigatran or edoxaban is needed. However, monitoring for increased side effects is recommended.
- US label recommends to use a reduced initial betrixaban dose of 80 mg followed by 40 mg qd.
- Dabigatran should be reduced to 100 mg bid in persons with normal renal function and to 75 mg bid in case of moderate renal impairment. Co-administration should be avoided in case of severe renal impairment.
- No significant increase in DRV/r exposure when administered simultaneously with dabigatran in persons with no renal impairment.
- European label advises to consider a dose reduction of edoxaban from 60 mg to 30 mg, however, US label recommends no dose modification.
- Unboosted ATV predicted to increase the anticoagulant. Monitor INR and adjust the anticoagulant dosage accordingly.
- Decreased conversion to active metabolite leading to non-responsiveness to clopidogrel. An alternative to clopidogrel should be considered.
- Increase in amount of active metabolite via induction of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6.
- Unboosted ATV predicted to increase dipyridamole exposure due to UGT1A1 inhibition.
- Reduced active metabolite, but without a significant reduction in prasugrel activity.
♥ EFV prolonged the QT interval above the regulatory threshold of concern in homozygous carriers of the CYP2B6*6/*6 allele (516T variant). Coadministration with a drug with a known risk of TdP is contraindicated in the EFV European label.
^ LEN causes moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and, when discontinued, remains in the circulation for prolonged periods. Residual concentrations of LEN may affect the exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates and/or narrow therapeutic index drugs that are initiated within 9 months after the last subcutaneous dose of LEN.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
