COVID-19 Therapies & ARVs
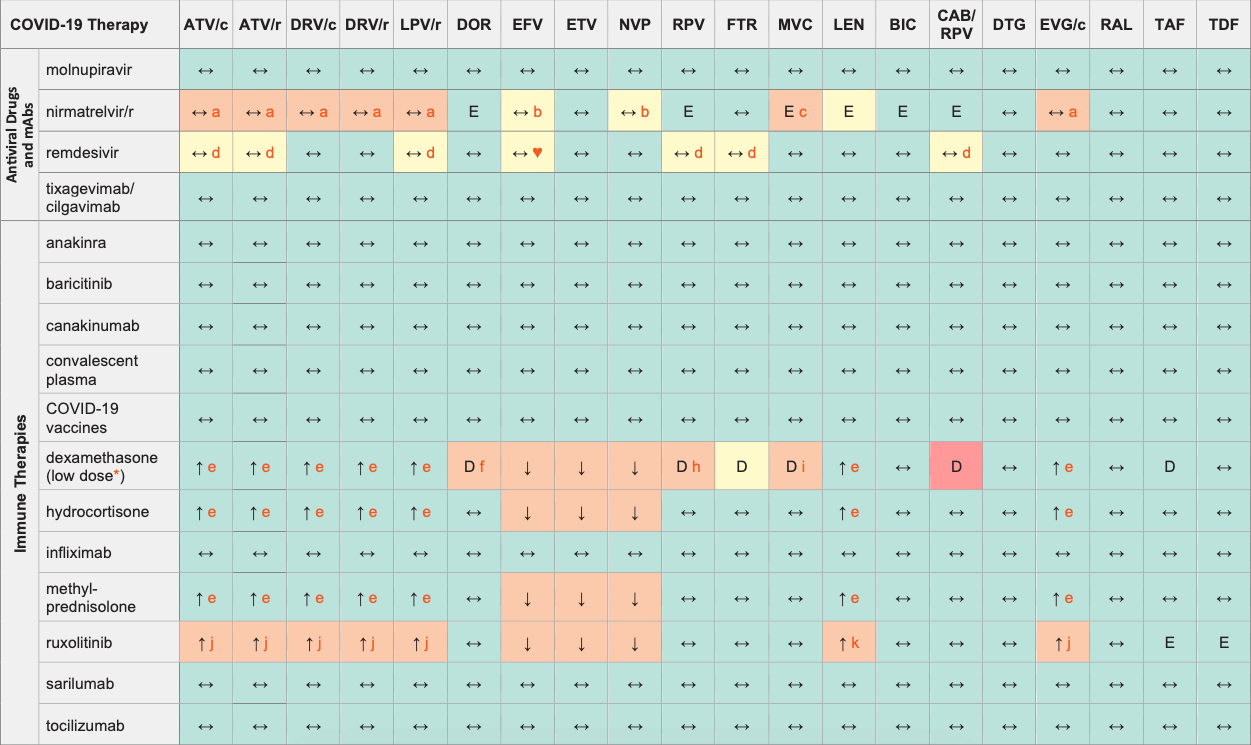

Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the COVID therapy
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the COVID therapy
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
* Evaluation of the DDI risk refers to a dexamethasone dose of 6 mg qd and does not apply to higher doses of dexamethasone.
mAbs (monoclonal antibodies)
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC, FTC, 3TC:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
ZDV:
Potential additive haematological toxicity with anakinra, baricitinib, canakinumab, ruxolitinib, sarilumab, tocilizumab
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- RTV or COBI containing regimens are continued with no dosage modification. Inform about potential occurrence of adverse effects.
- Ritonavir bid is expected to counteract the inducing effect of EFV, NVP.
- Consider using MVC at a dose of 150 mg bid.
- Remdesivir has a possible risk of QT prolongation and/or TdP on the CredibleMeds.org website.
- Product labels for dexamethasone, hydrocortisone and methylprednisolone do not recommend co-administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors but this is unlikely to be clinically significant given the low dose of corticosteroids used in COVID-19 treatment.
- Consider increasing DOR to 100 mg bid during treatment for COVID-19 and for approximately 2 weeks after the end of treatment.
- Doubling the dose of dexamethasone, hydrocortisone or methylprednisolone is recommended.
- Dexamethasone is a dose dependent CYP3A4 inducer and may decrease RPV concentrations. Although the level of induction at the dose recommended for COVID (6 mg/day) is likely to be relatively modest, it is advised either using hydrocortisone (IV, 200 mg/day) or, alternatively, giving dexamethasone but doubling the dose of RPV to 50 mg qd. This dose should be maintained for 2 weeks after the end of treatment as any reduction in RPV concentrations may persist for up to 14 days after stopping dexamethasone.
- Consider using MVC at a dose of 600 mg bid with dexamethasone in the absence of a PI or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider decreasing MVC to 150 mg bid with dexamethasone in presence of a PI or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. These dose adjustments should be considered during treatment for COVID-19 and for approximately 2 weeks after the end of treatment.
- The ruxolitinib European product label advises reducing ruxolitinib dose by half and administering bid. Monitor closely for cytopenia and titrate ruxolitinib based on safety and efficacy.
- Monitor closely for cytopenia.
♥ EFV prolonged the QT interval above the regulatory threshold of concern in homozygous carriers of the CYP2B6*6/*6 allele (516T variant). Coadministration with a drug with a known risk of TdP is contraindicated in the EFV European label.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.covid19-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
