Bronchodilators & ARVs
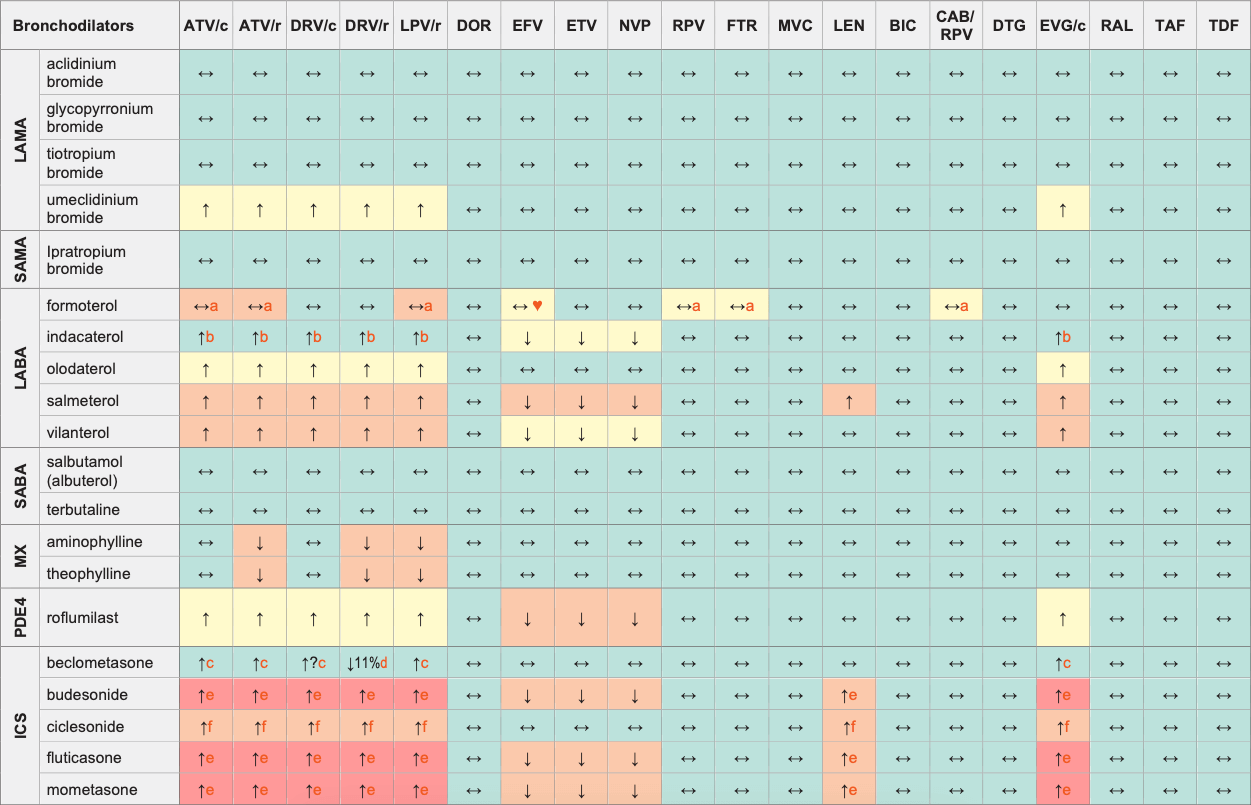

Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the bronchodilator
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the bronchodilator
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
ICS (inhaled corticosteroids)
LABA (long-acting β2 agonists)
LAMA (long-acting muscarinic antagonists)
MX (methylxanthines)
PD4 (phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors)
SABA (short-acting β2 agonists)
SAMA (short-acting muscarinic antagonists)
Note
Fixed dose combinations are available for LAMA + LABA + ICS, e.g.,
- mometasone + indacaterol + glycopyrronium
- fluticasone + umeclidinium + vilanterol
- formoterol + glycopyrronium + beclometasone
- budesonide + formoterol + glycopyrronium
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- Caution as both drugs can induce QT interval prolongation.
- Exposure can be increased up to 2-fold however this increase does not raise any concerns based on indacaterol's safety data.
- Increase in concentration of active metabolite observed with RTV 100 mg bid alone but without significant effect on adrenal function. Caution is still warranted, use the lowest possible corticosteroid dose and monitor for corticosteroid side effects.
- DRV/r decreased the exposure of active metabolite (beclometasone-17- monopropionate), no significant effect on adrenal function was seen.
- Risk of having elevated corticosteroid levels, Cushing's syndrome and adrenal suppression. This risk is present for oral and injected corticosteroid but also for topical, inhaled or eye drops administration.
- No dose adjustment required but monitor closely, especially for signs of Cushing's syndrome when using a high dose or prolonged administration.
♥ EFV prolonged the QT interval above the regulatory threshold of concern in homozygous carriers of the CYP2B6*6/*6 allele (516T variant). Coadministration with a drug with a known risk of TdP is contraindicated in the EFV European label.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
