Anti-malarial Drugs & ARVs
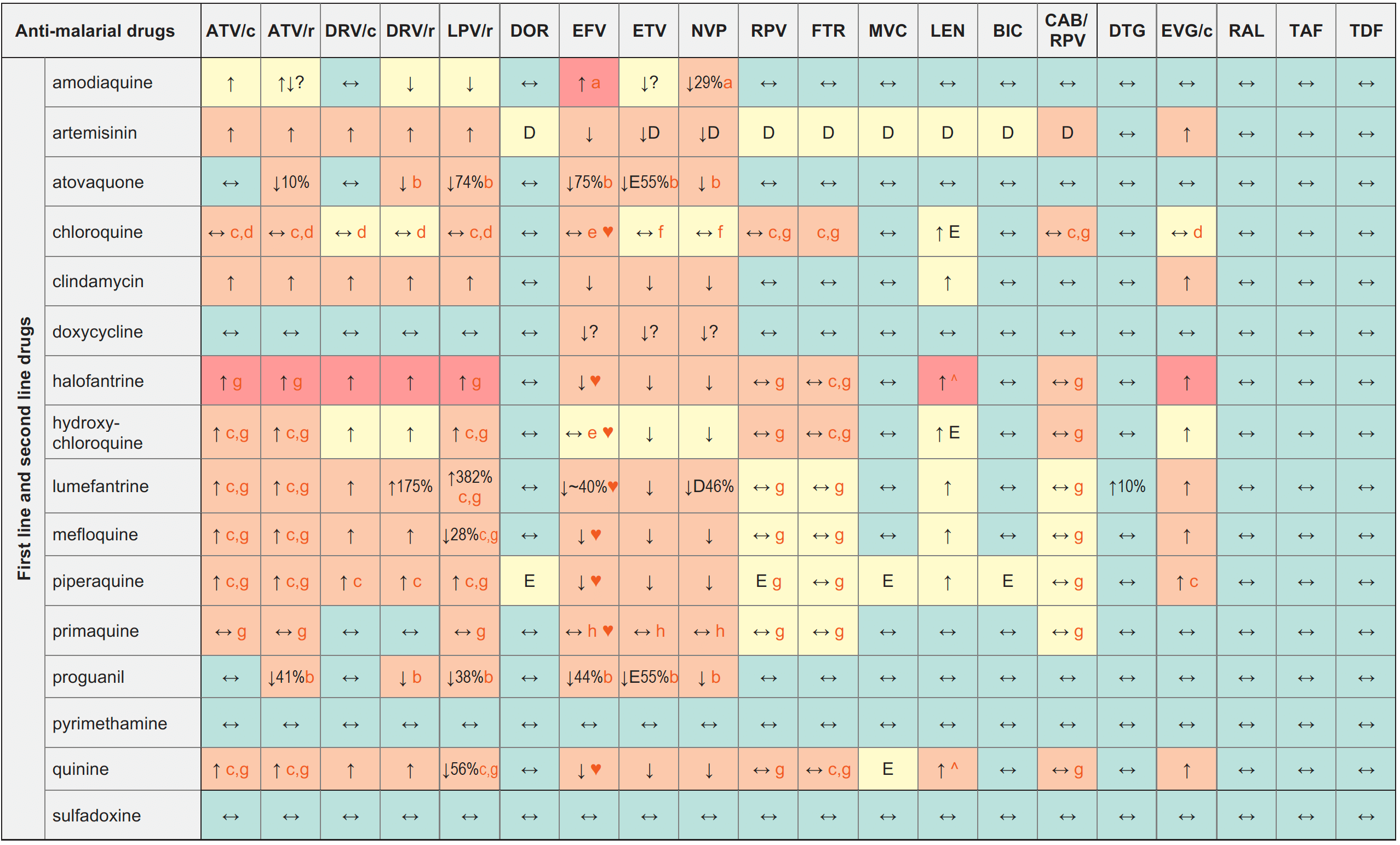
Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the anti-malarial drug
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the anti-malarial drug
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
FTC:
Increased FTC exposure with pyrimethamine, sulfadoxine
3TC:
Increased 3TC exposure with pyrimethamine, sulfadoxine
ZDV:
Potential additive haematological toxicity with amodiaquine, atovaquone, primaquine, pyrimethamine, sulfadoxine
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- Liver toxicity.
- Take with high fat meal, consider dose increase.
- ECG monitoring is recommended.
- Chloroquine concentrations may increase, but to a moderate extent. No dose adjustment is required but monitor toxicity.
- Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine concentrations may increase or decrease. No dose adjustment is required but monitor toxicity and efficacy.
- Chloroquine concentrations may decrease, but to a moderate extent. No dose adjustment is required but monitor efficacy.
- Caution as both drugs can induce QT interval prolongation.
- Increase of haemotoxic metabolites.
♥ EFV prolonged the QT interval above the regulatory threshold of concern in homozygous carriers of the CYP2B6*6/*6 allele (516T variant). Coadministration with a drug with a known risk of TdP is contraindicated in the EFV European label.
^ LEN causes moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and, when discontinued, remains in the circulation for prolonged periods. Residual concentrations of LEN may affect the exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates and/or narrow therapeutic index drugs that are initiated within 9 months after the last subcutaneous dose of LEN.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
