Increased ALT/AST: Work-up & Management
Identify potential cause of increased liver enzymes, using the following steps:
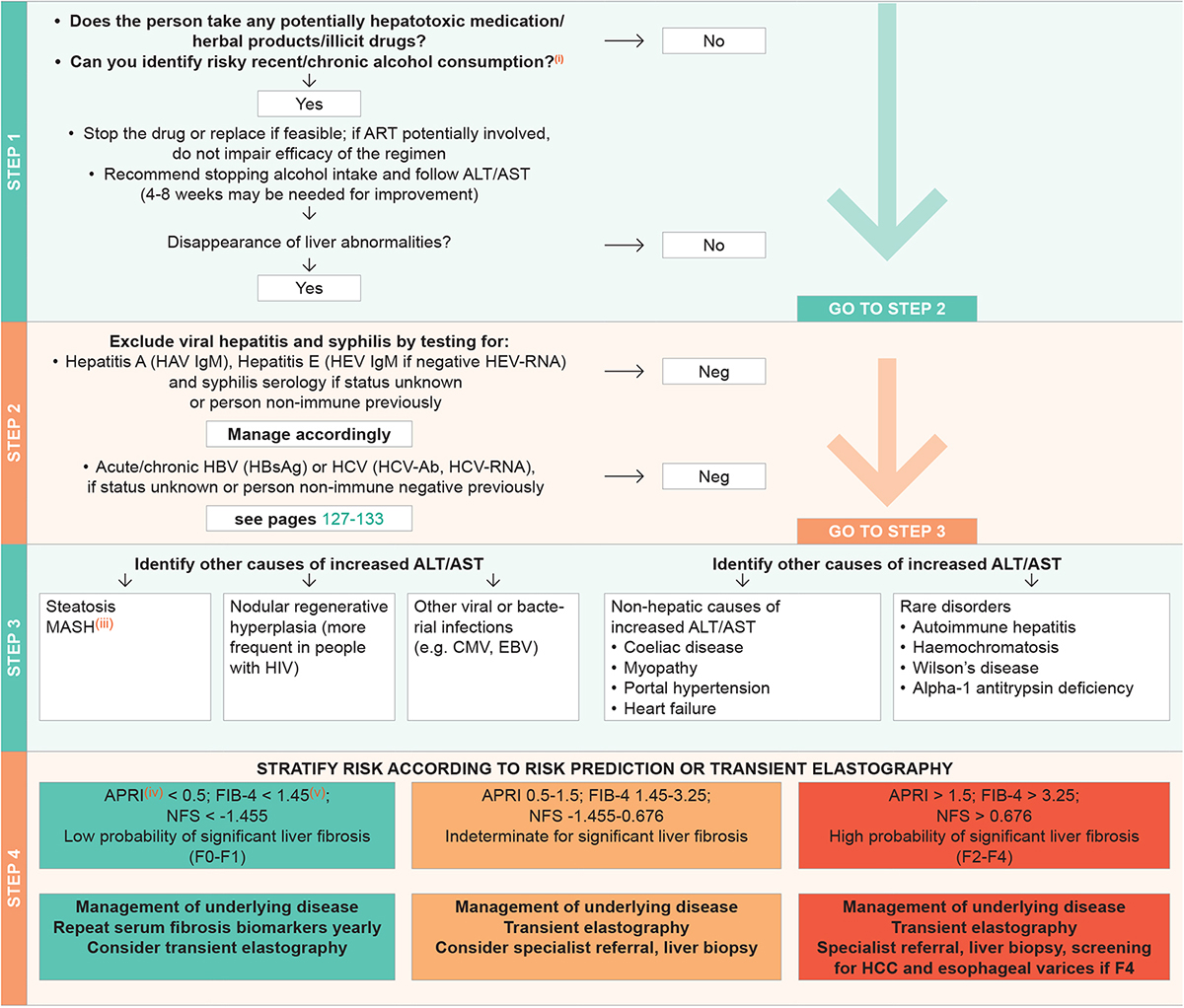
* In chronic Hepatitis B, we recommend the use of APRI or transient elastography. An APRI score >0.5 or transient elastography value >7 kPa identify most adults with significant liver fibrosis. An APRI >0.5 is recommended as a key criterion for giving priority to initiating antiviral therapy in resource-limited settings.
See Liver Cirrhosis: Classification and Surveillance
See Liver Cirrhosis: Management
See Dose Adjustment of ARVs for Impaired Hepatic Function
- > 20 g in women, > 30 g in men
- Reflex anti-Hepatitis delta (HDV) testing if a patient is HBsAg positive
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, see MASLD
- APRI, AST to Platelet Ratio Index = (AST in IU/L) / (AST Upper Limit of Normal in IU/L) / (Platelets in 109/L)
- FIB-4 = Age [years] x AST [U/L])/platelet [109/L] x ALT1/2 [U/L]). For MASLD aetiology FIB-4 cut offs are as follows: < 1.30 (low risk), > 2.67 high risk.
FIB-4 cut off < 2.0 (instead of < 1.30) should be considered in persons aged > 65 years
