Cognitive Impairment
Algorithm for Diagnosis and Management of Cognitive and Central Nervous System Neurological Symptoms
Abbreviations
CSF = cerebrospinal fluid
CNS = central nervous system
GDR = genotypic drug resistance test
HAD = HIV-associated dementia
LOQ = Limit of quantification
MND = mild neurocognitive disorders
MRI = brain magnetic resonance imaging
NP = neuropsychological
OIs = opportunistic infections
RCT = randomised controlled trial
Algorithm
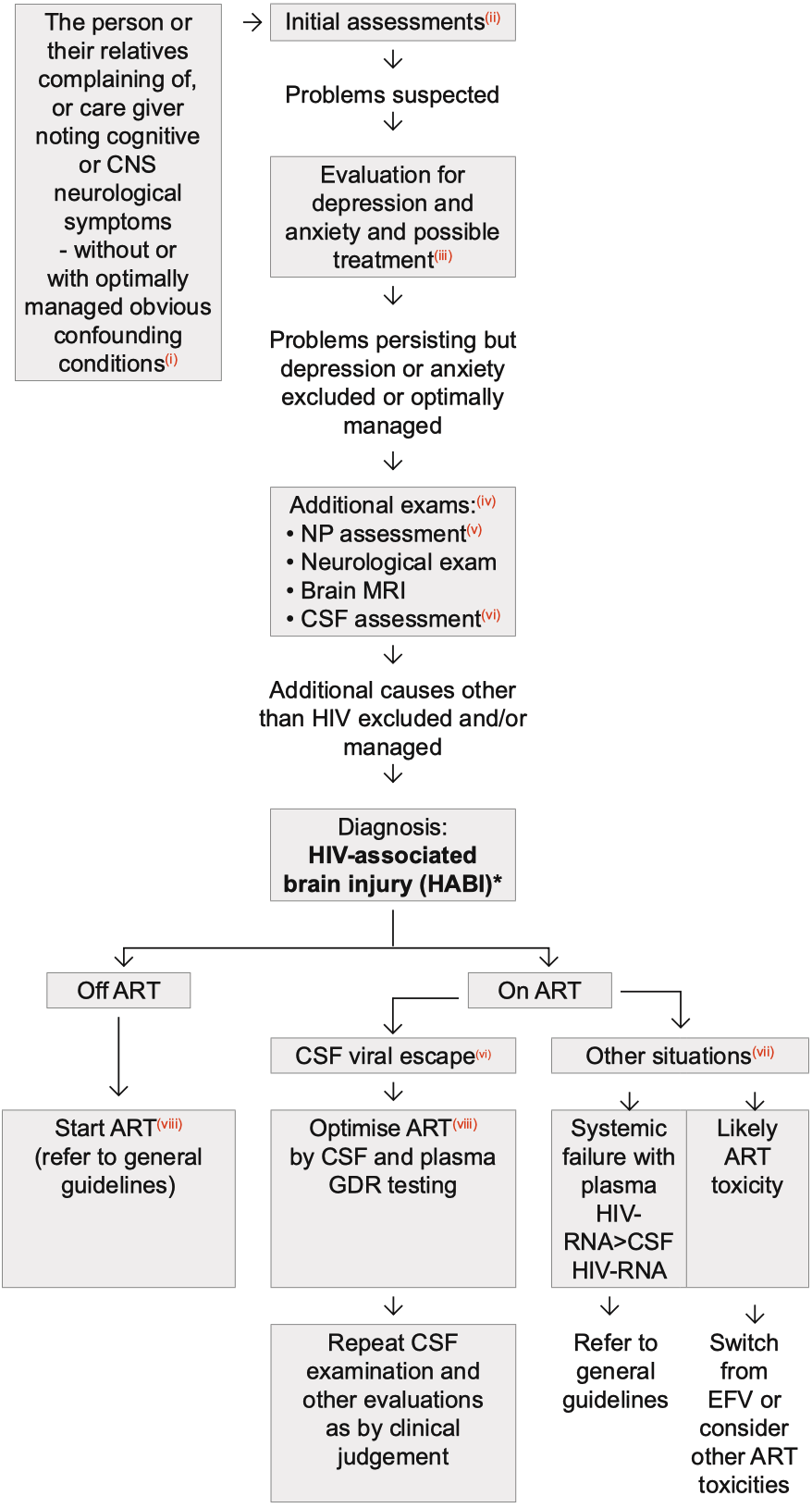
i Obvious confounding conditions:
- Severe psychiatric conditions
- Use of drugs that can impair cognitive function, such as anticholinergic (e.g. amitriptyline, chlorpromazine) or psychotropic drugs
- Alcohol abuse
- Sequelae from previous CNS-OIs, pre-treatment cognitive disease or other neurological diseases
- Current CNS-OIs or other neurological diseases
ii The following questions may be used to guide initial assessments of cognitive symptoms (other screening assessments are also acceptable)
- Do you experience frequent memory loss (e.g. do you forget the occurrence of special events even the more recent ones, appointments, etc.)?
- Do you feel that you are slower when reasoning, planning activities, or solving problems?
- Do you have major difficulties paying attention (e.g. to a conversation, book or film)?
Answering “yes” to one or more of these questions may suggest the presence of cognitive disorders, although not necessarily linked to HIV.
iii See Depression: Screening and Diagnosis and Anxiety Disorders: Screening and Diagnosis
iv NP assessment, neurological exam, brain MRI and CSF assessment are required to diagnose other pathologies (consultation with neurologist specialist may be required) and to further characterise possible HIV-associated brain injury (HABI)
v NP assessment should be considered where cognitive symptoms are present and ideally include tests exploring the following cognitive domains: fluency, executive functions, speed of information processing, attention/working memory, verbal and visual learning, verbal and visual memory, motor skills plus assessment of daily functioning. Cognitive impairment is defined by impairment in cognitive function on the above neuropsychological test where performance is compared to age- and education-matched appropriate controls and is considered clinically significant
vi CSF escape definition:
Either CSF HIV-RNA above LOQ and plasma HIV-RNA below LOQ; or HIV-RNA above LOQ in both CSF and plasma, with CSF HIV-RNA greater than plasma HIV-RNA. In CSF escape:
- Avoid dual ART therapies
- Include dual nucleoside backbones in ART regimens where possible
- Avoid ATV (boosted or unboosted) due to association with CSF escape in retrospective cohorts
- Avoid RAL 1200 mg qd due to lack of evidence in CSF escape
- Consider DTG 50 mg bid in cases with documented or suspected INSTI resistance
vii Including situations that do not fulfill the CSF escape definition, but can benefit from ART optimization
viii Avoid EFV because of its possible effects on cognitive function and potentially confounding CNS effects due to neuropsychiatric effects
*Nightingale S, Ances B, Cinque P et al. Cognitive impairment in people living with HIV: consensus recommendations for a new approach. Nat Rev Neurol . 2023 Jul;19(7):424-433.
