ARV Dosing: Renal Impairment
Dose Adjustment of ARVs for Impaired Renal Function
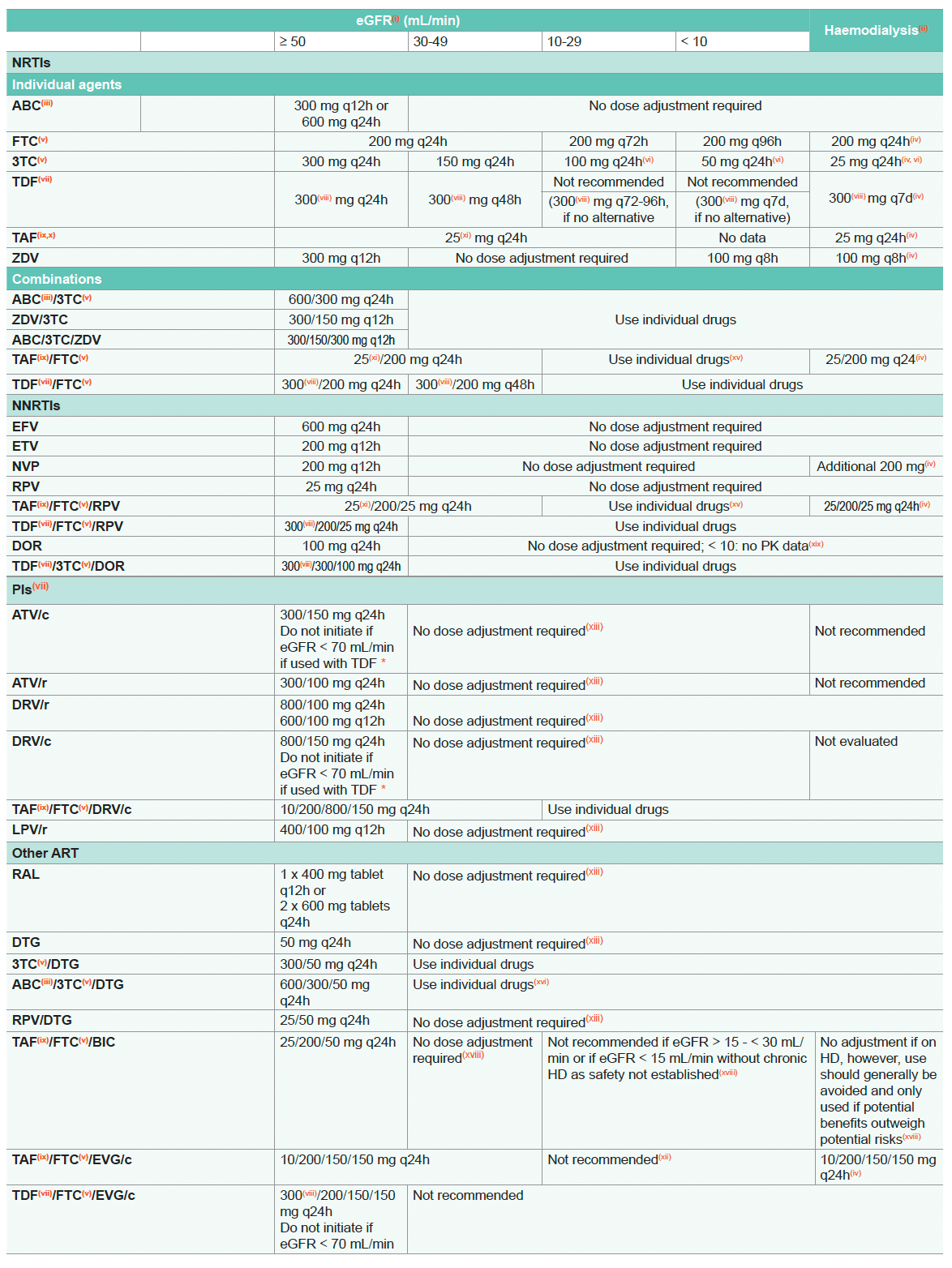
- eGFR: Use CKD-EPI formula; the abbreviated modification of diet in renal disease (aMDRD) or the Cockcroft-Gault (CG) equation may be used as an alternative; see www.chip.dk/Tools-Standards/Clinical-risk-scores
- For Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) dosing for hemodialysis may be used. However, elimination of drugs in CAPD varies depending on CAPD conditions, NRTI may accumulate. TDM therefore is recommended
- Potential cardiovascular risk of ABC may increase cardiovascular risk associated with renal failure
- After dialysis
- Large bodily accumulation in impaired renal function. Although affinity for mitochondrial DNA polymerase is low and clinical toxicity in patients with severe renal impairment is rare, long-term mitochondrial toxicity is possible and must be monitored (polyneuropathy, pancreatitis, lactate acidosis, lipodystrophy, metabolic disturbances)
- 150 mg loading dose; 50 mg loading dose for haemodialysis
- TDF and (boosted) PIs are associated with nephrotoxicity; consider alternative ART if pre-existing CKD, risk factors for CKD and/or decreasing eGFR, see ARV-associated Nephrotoxicity and Kidney Disease: Definition, Diagnosis and Management
- In certain countries TDF is labelled as 245 mg rather than 300 mg to reflect the amount of the prodrug (tenofovir disoproxil) rather than the fumarate salt (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate)
- Limited clinical data documented limited accumulation in hemodialysis. However, there is no long-term data on residual kidney function and bone toxicity. No data for eGFR < 10 mL/min but no dialysis
- Only licenced for HBV
- 10 mg if co-administered with a boosting agent (inhibition of P-glycoprotein, P-gp)
- TAF/FTC/EVG/c as a single tablet regimen should generally be avoided in persons with end-stage renal disease on chronic dialysis. However, TAF/FTC/EVG/c may be used with caution if the potential benefits are considered to outweigh potential risks. One clinlical study has demonstrated safety of TAF/FTC/EVG/c for persons on chronic dialysis
- Limited data available in persons with renal impairment; pharmacokinetic analysis suggests no dose adjustment required
- See summary of product characteristics for specific recommendations; use with caution if eGFR ≤ 30 mL/min. 10 mg if co-administered with a boosting agent (inhibition of P-glycoprotein, P-gp)
- TAF/FTC and TAF/FTC/RPV single tablet regimens should generally be avoided in persons with end-stage renal disease on chronic dialysis. However, these combinations may be used with caution if the potential benefits are considered to outweigh potential risks
- ABC/3TC/DTG as a single tablet regimen should generally be avoided in persons with end-stage renal disease on chronic haemodialysis. A recent case series study found that use of ABC/3TC/DTG appears to be a safe and effective option in persons on chronic dialysis, however these findings need to be confirmed in a larger trial
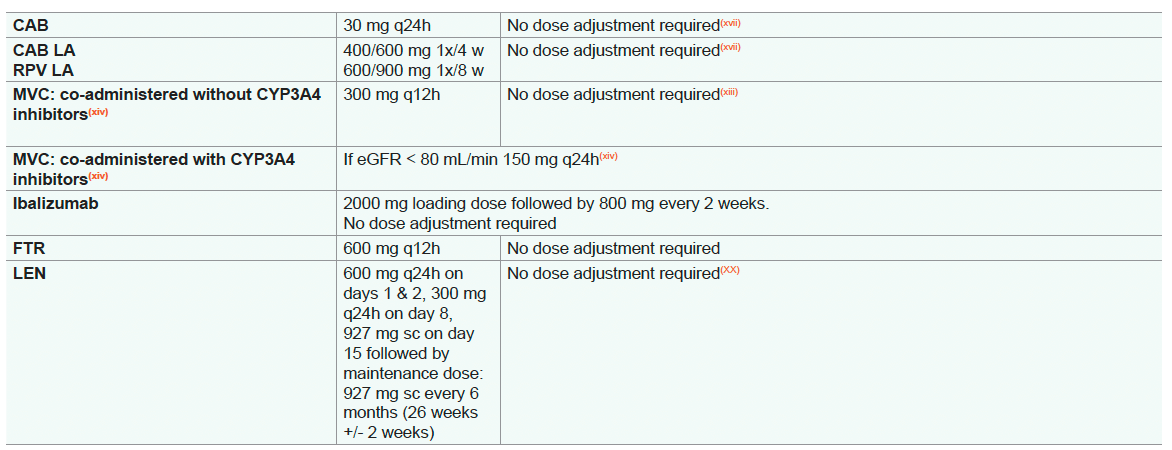
- In persons with eGFR < 30 mL/min, co-administration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (e.g. ketoconazole, posaconazole) should be used only if the benefit outweighs the risk
- According to the product label
- Doravirine is modestly removed by haemodialysis so that no dosage adjustment is needed
- LEN has not been studied in individuals with end stage renal disease (CrCL <15 mL/min or on renal replacement therapy and therefore should be used with caution in these individuals)
* Due to lack of COBI data in persons with HIV with renal impairment
For recommendations on ART use in persons with HIV undergoing renal transplantation, see Solid Organ Transplantation
