Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) & ARVs
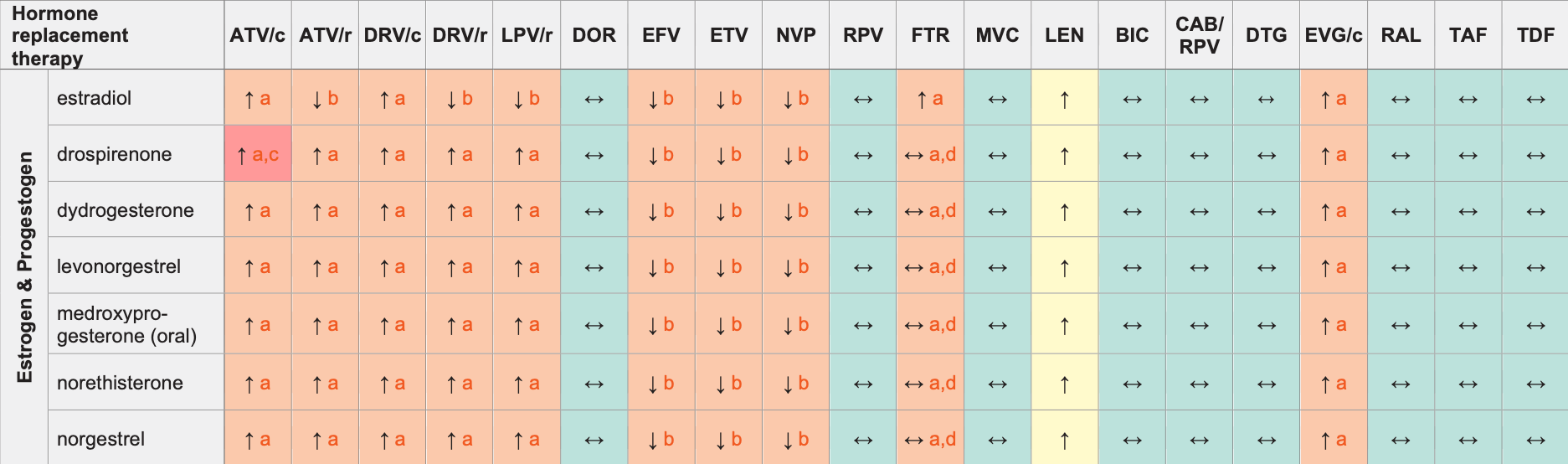

Legend
↑ Potential elevated exposure of the hormone
↓ Potential decreased exposure of the hormone
↔ No significant effect
D Potential decreased exposure of ARV drug
E Potential elevated exposure of ARV drug
Numbers refer to increased or decreased AUC as observed in drug-drug interaction studies
ATV/c:
ATV co-formulated with COBI (300/150 mg qd)
DRV/c:
DRV co-formulated with COBI (800/150 mg qd)
CAB/RPV:
CAB and RPV im long acting injections
Interactions with ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV
ABC, FTC, 3TC, ZDV:
No clinically relevant interactions expected
Interactions with cabotegravir (oral)
None
Interactions with ibalizumab
None
Comments
- The clinical significance of increased estradiol exposure in terms of overall risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, stroke and myocardial infarction in postmenopausal women receiving substitution hormones in unknown. The use of estrogen alone or in combination with a progestogen should be used at the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for individual women. Postmenopausal women should be re-evaluated.
- Monitor for signs of estrogen deficiency.
- Co-administration is contraindicated in the US product label due to the potential for hyperkalaemia. The European product label recommends clinical monitoring for hyperkalaemia.
- No effect on progestogen but potential increase in estrogen exposure.
Further Information
For additional drug-drug interactions and for more detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, please refer to: http://www.hiv-druginteractions.org (University of Liverpool)
